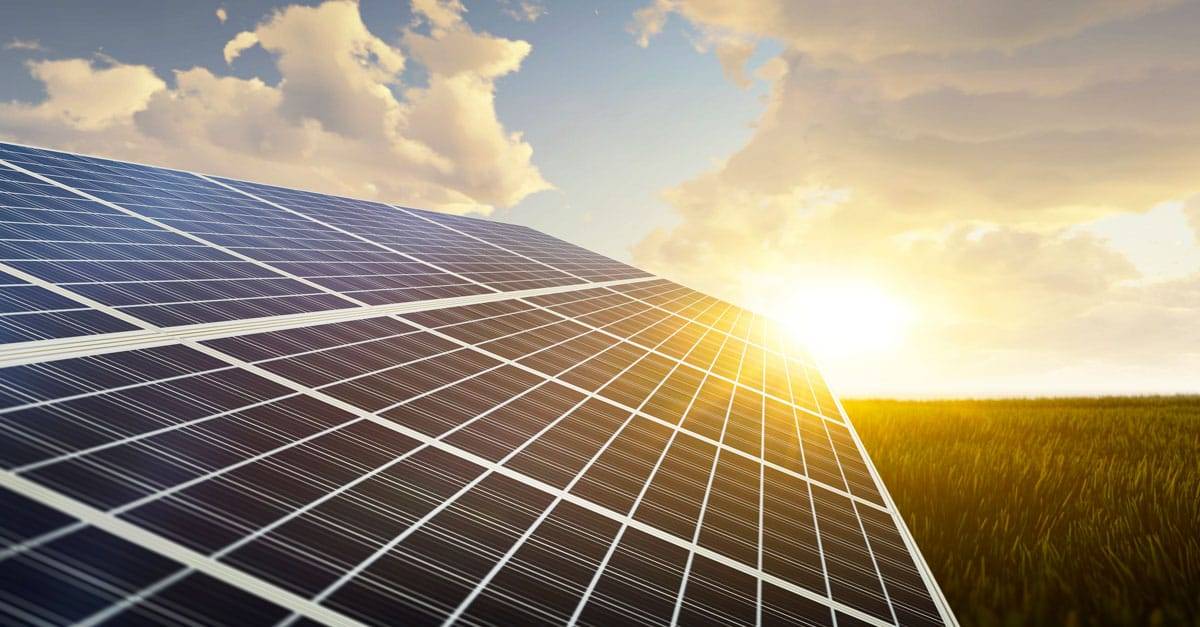
“Plastic” or “plastic solar cells” are other names for organic solar cells because they are made of hydrocarbon compounds. The function of organic solar cells is the same as that of crystalline modules in photovoltaics (PV). As soon as sunlight hits the organic semiconductor, electrons dissociate from their connections, and there is a current flow.
Various Uses
One can say that organic solar cells form a special version of thin-layer solar modules. Due to their special electron structure, they have similar properties to amorphous silicon semiconductors.
It is possible to use the flexible cells not only on curved roofs but also on carcasses or other curved surfaces. They are environmentally friendly, lightweight, and, above all, flexible. The new solar cells can be integrated into glass facades and windows, as they absorb only a fraction of the visible light.
According to Transparency Market Research, a US market researcher, the market volume of organic solar cells will still be 97 million USD in 2020. It is forecast to reach 807 million USD by 2031. That’s a relatively small amount compared to other future technologies. However, there is a possibility that it may increase significantly if the efficiency of organic solar cells is higher.
Elevate Your Wealth Game: Empowering UHNWIs for Simplified Asset Management. Altoo Platform Preview
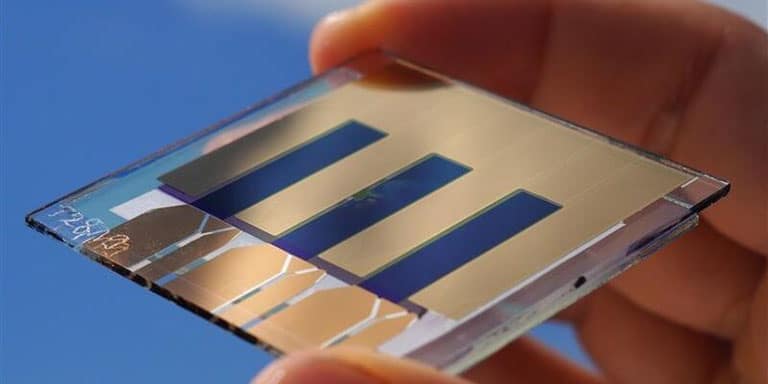
Fraunhofer ISE: World Record in Efficiency
Currently, the efficiency of organic solar cells in mass production is less than 10%, which typically ranges from 7% to 9%. But science is busy with the new technology, because the hopes for organic photovoltaics are high. Recently, researchers at the German Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) have set a new world record. The efficiency of an organic solar cell of one square centimetre was improved to 15.8% in collaboration with the FMF research centre of the University of Freiburg.
In comparison, traditional silicon modules convert 20% of solar energy into electricity. This is also the reason why, despite their advantages, the cells are not yet widely used.
Organic solar cells are a cost-effective and flexible alternative to crystalline modules, but they have low performance and a shorter life. However, their technical capabilities have not yet been exhausted. Unlike crystalline solar cells, whose efficiency cannot be increased by more than 30% in principle, there is no theoretical power limit for organic cells.
So in theory, the potential of these organic solar cells is enormous. Whether, in the near future, the technology will be enough to make it practical is another question.









